Our Technology
Drug Delivery into the Brain
Our technology, a ligand (navigation molecule) -modified polymer nanoparticle composition, allows drugs to be transported into the brain across the blood-brain barrier through a mechanism of action known as transcytosis.
Braizon’s nano-scale, safe, and biodegradable carriers extend circulation within the body and protect them from the drug removal mechanism of the BBB after transport into the brain. The process to package drugs within our carriers can be simple and not affect the pharmacological activity of the active compound. These carriers are engineered to fit their purpose and will release their cargo at the intended site.
This occurs either in response to the local environment between the cells of the brain for extracellular release, or the reduced pH conditions within the endosomes of target cells for intracellular release.
Please see the video below. You could understand the mechanism of our DDS technology.
Our company is also studying the TfR pathway in addition to the GLUT1 pathway. This video is an animation that illustrates the mechanism of the GLUT1 pathway. In the case of the TfR pathway, glycemic control such as dietary restriction is not required.
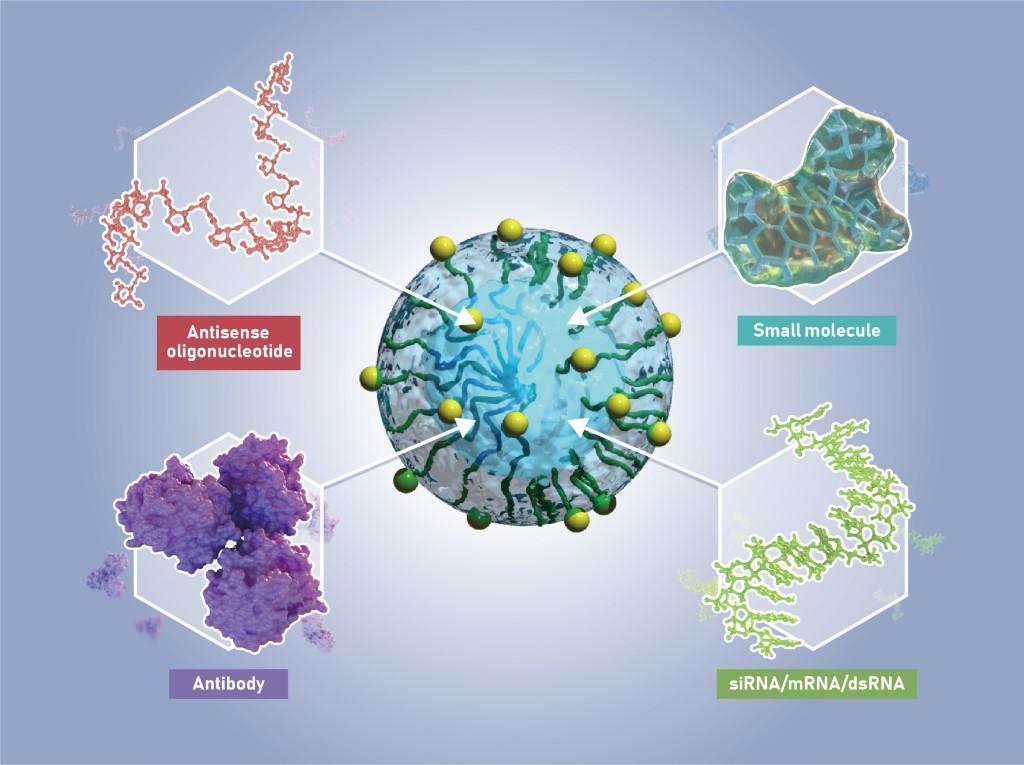
Platform Capabilities
Braizon’s Drug Delivery System is highly versatile and offers the potential to deliver a wide range of therapeutic compounds, from small molecules to biologics, into the brain and spinal cord. Our glucosylated nanoparticles can enclose even high molecular weight or poorly stable molecules inside a protective polymer capsule. In cases where it may be necessary to optimize the structure of the carrier polymers to best fit the delivery needs of a therapeutic molecule, Braizon’s deep expertise in formulation can readily provide the most favorable solution.
Related papers
| Therapeutic Molecule | Article |
|---|---|
| Antisense Oligonucleotides | Targeting the Notch-regulated non-coding RNA TUG1 for glioma treatment Katsushima, Kataoka, et al. Nat Commun. 2016, 3616 |
| Summary | |
| Anti-sense Oligonucleotides targeting TUG1 coupled with a drug delivery system of cRGD peptide conjugated polymeric micelles | |
| Therapeutic Molecule | Article |
| mRNA | Modulated Protonation of Side Chain Aminoethylene Repeats in N-Substituted Polyaspartamides promotes mRNA Transfection Uchida, Kataoka, et al, J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 12396-12405 |
| Summary | |
| Fine-tuning of chemical structure of polycation-based-carriers for safe and efficient mRNA transfection | |
| Therapeutic Molecule | Article |
| Antibody | Intracellular Delivery of Charge-Converted Monoclonal Antibodies by Combinatorial Design of Block/Homo Polyion Complex Micelles Kim, Kataoka et. al. Biomacromolecules, 2016, 17, 446–453 |
| Summary | |
| Polyion Complex (PIC) including Antibody micelles by optimization of charge-conversional degree | |
| Therapeutic Molecule | Article |
| Small Molecule | cRGD peptide-installed epirubicin-loaded polymeric micelles for effective targeted therapy against brain tumors Quader, Kataoka, et al, J. Control. Rel., 2017, 258, 56-66 |
| Summary | |
| Epirubicin (Anti-cancer drug) loaded micelles using Acetal-PEG- PBLA (poly benzal-aspartamide) | |
「Illustration creator and cooperation: VESPERSTUDIO Inc.」
Publication
The following manuscript describes the basis of Braizon’s technology and was published by our scientific advisors in 2017.
Published by Springer Nature: Anraku, Y. et al. (2017) Glycaemic control boosts glucosylated nanocarrier crossing the BBB into the brain. Nature Communications 8: 1001-1009 Licensed under CC BY 4.0
Anraku. Y. et al. (2017) NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 8: 1001-1009 SPRINGER NATURE
